Functional Skills: Division
Division
Division is splitting up a number or object into pieces that are the same size. The most common method used to divide large numbers without a calculator is the bus stop method. If you have a calculator, then division problems are more straightforward, but can still be a little tricky – some questions need whole number answers.
Make sure you are happy with the following topics before continuing.
When to Divide
You need to know when a question requires you to divide. There are two things to look out for:
- Questions involving the words “divide” or “division” or similar.
- Questions involving the divide sign, \div.
Division can also sneak into questions, for example through fractions or through wordy questions that give you a total and ask for a part of the total. This will be seen many times in this course.
Follow Our Socials
Our Facebook page can put you in touch with other students of your course for revision and community support. Alternatively, you can find us on Instagram or TikTok where we're always sharing revision tips for all our courses.
Bus Stop Method
This method of division is called the bus stop method, because it looks like the shape of a bus stop. You can divide numbers to find whole number answers, decimal answers, or answers that have a remainder.
Example: Work out 288 \div 9, without using a calculator.
Step 1: Firstly, put the division into the Bus Stop seen below.

Step 2: See how many times 9 goes into the first digit, 2, which is \textcolor{limegreen}{0} times, so the \textcolor{red}{2} is carried to the next digit to make 28. The 0 goes above the bus stop.
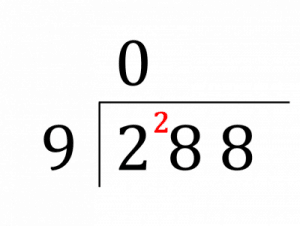
Step 3: Next, see how many times 9 goes into 28. We know 3 \times 9=27, so 9 goes into 28 \textcolor{limegreen}{3} times with a remainder
\textcolor{red}{1}, which is carried in front of the next digit to make 18. The 3 goes on top.
Step 4: Then, see how many times 9 goes into 18, which is \textcolor{limegreen}{2} times. The 2 goes above the bus stop.
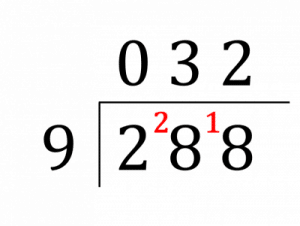
So, the answer is,
288 \div 9 = \textcolor{blue}{32}
Notes:
If in the last step of the division the number does not divide into it fully, then we can either:
add a decimal point and extra 0‘s at the end of the number that is being divided
e.g. Calculate 315 \div 14
\;\;\;\;\;0\;2\;2\;.\;5 \\ 14\overline{\left) 3{}^31{}^35.{}^70 \right.}
or say the answer with a remainder on the end
e.g. Calculate 315 \div 14
\;\;\;\;\;\;\;\;\;\;\;\;0\;2\;2 \;\; \text{ r } 7 \\ 14\overline{\left)3{}^31{}^35 \right.}
Dividing on a Calculator
The Bus Stop Method is for dividing without a calculator. Dividing with a calculator is significantly simpler. All you do is type the digits of one number, then press the divide symbol \div, then type the digits of the other number, then press equals.
Example: Use a calculator to find 5040 divided by 336.
Press 5 then 0 then 4 then 0 then \div then 3 then 3 then 6 then =.

Your calculator should give an answer of 15.
Dividing by \boldsymbol{10}, \boldsymbol{100}, \boldsymbol{1000}...
Dividing by powers of 10 is very similar to multiplying, except instead of moving the decimal point to the right, you move it to the left. The amount of times you move the decimal point depends on the amount of zeros.
- To divide by \textcolor{purple}{\boldsymbol{10}}, you move the decimal point one place to the left.
- To divide by \textcolor{purple}{\boldsymbol{100}}, you move the decimal point two places to the left.
- To divide by \textcolor{purple}{\boldsymbol{1000}}, you move the decimal point three places to the left.
Remember: For whole numbers the decimal point doesn’t look like it’s there, but it is. For example 25 can be written as 25.0
Checking Your Answer
Dividing is the opposite of multiplying. This means that, now we know how to do both, we can do one to check the other.
Example: Find 1536\div3, then perform a suitable check of your answer.
Use a calculator for this to find that 1536\div3=512
We can check this by multiplying 512 and 3 to make sure we get back to 1536
Use a calculator for this to find that 512\times3=1536
Example: Find 82\times21, then perform a suitable check of your answer.
Use a calculator for this to find that 82\times21=1722
We can check this by dividing 1722 by 21 to make sure we get back to 82
Use a calculator for this to find that 1722\div21=82
Example 1: Division with Remainder
Work out 67 \div 5, without using a calculator.
[2 marks]
Use the bus stop method shown before. However, there is now a remainder.

Therefore,
67 \div 5 = \textcolor{blue}{13} \text{\textcolor{black}{ r }} \textcolor{red}{2}
Example 2: Division Problems
Peter needs to buy some tiles for his bathroom. Tiles come in packs of 18, and he needs 99 tiles.
How many packs of tiles does Peter need?
[2 marks]
99 \div 18 = \textcolor{blue}{5.5}
He can’t buy \textcolor{blue}{5.5} packs of tiles, so the answer must be a whole number.
There wont be enough tiles if he buys 5 packs (since 5 \times 18 = 90), so he will need to buy \textcolor{blue}{6} packs and have 9 left over.
Example 3: Dividing by \boldsymbol{10}, \boldsymbol{100}, \boldsymbol{1000}...
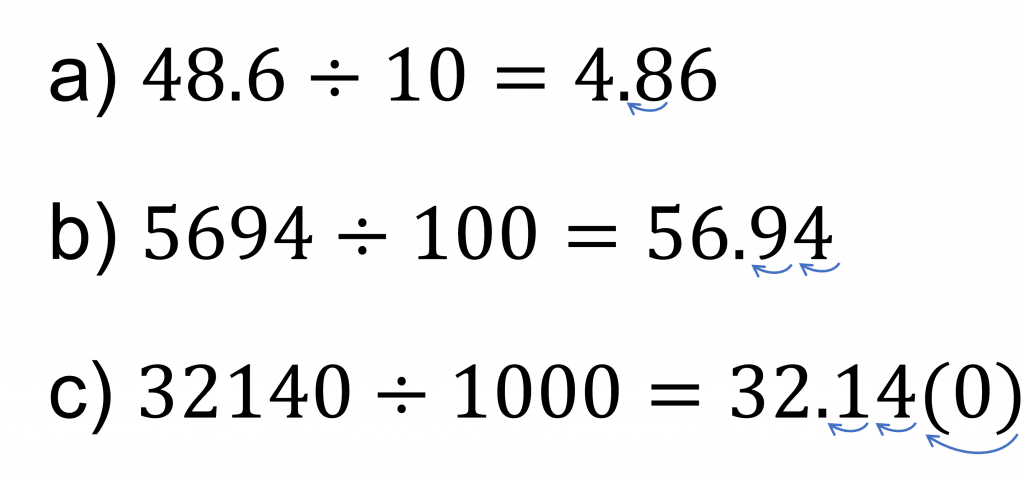
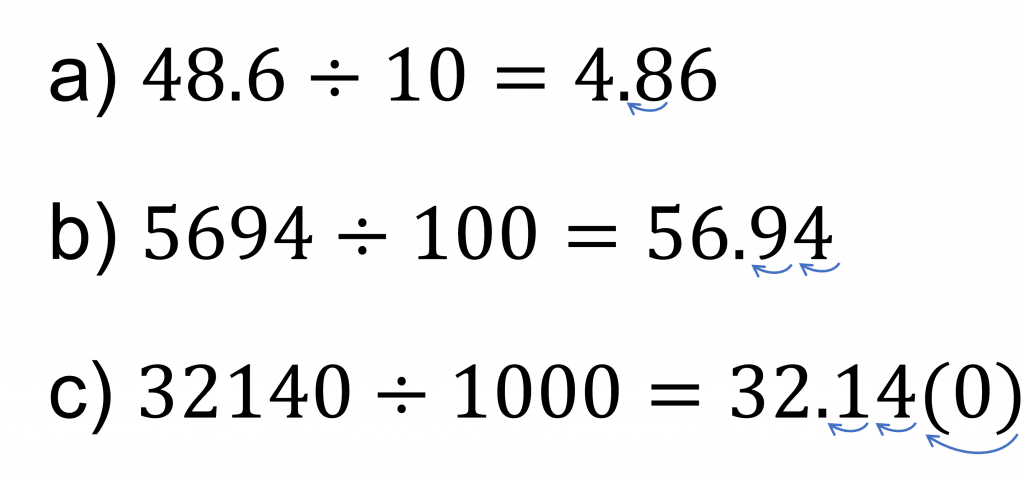
Calculate:
a) 48.6\div10
b) 5694\div100
c) 32140\div1000
[3 marks]
Functional Skills: Division Example Questions
Question 1: Calculate 225 \div 15, without using a calculator.
[2 marks]
Use the bus stop method:
\;\;\;\;\;0\;1\;5\\15\overline{\left)2{}^22{}^75\right.}
So, 225 \div 15 = 15
Question 2: Calculate 4320 \div 160, without using a calculator.
[2 marks]
Use the bus stop method:
\;\;\;\;\;\;\;0\;\;0\;\;2\;\;7\\160\overline{\left)4{}^43{}^{43}2{}^{112}0\right.}
So, 4320 \div 160 = 27
Question 3: For a school trip, one coach holds 75 people. There are 456 people going on the school trip.
How many coaches are needed altogether?
[2 marks]
456 \div 75 = 6.08
There can’t be 6.08 coaches, since the number of coaches needs to be a whole number.
6 coaches would not be enough to hold everyone (since 6 \times 75 = 450), so they need 7 coaches.
Question 4: Calculate the following:
a) 314.3\div10
b) 89741.1\div1000
c) 4563281\div100000
[3 marks]
a) Dividing by 10 means we move the decimal point one place to the left.
So
314.3\div10=31.43
b) Dividing by 1000 means we move the decimal point three places to the left.
So
89741.1\div1000=89.7411
c) Dividing by 100000 means we move the decimal point five places to the left.
So
4563281\div100000=45.63281
Specification Points Covered
EL3.3 – Divide three-digit whole numbers by single and double digit whole numbers and express remainders
L1.3 – Multiply and divide whole numbers and decimals by 10, 100, 1000
L1.4 – Use multiplication facts and make connections with division facts
L2.2 – Carry out calculations with numbers up to one million including strategies to check answers including estimation and approximation
Functional Skills: Division Worksheet and Example Questions
Division EL3
Entry Level 3NewOfficial PFSDivision L1
FS Level 1NewOfficial PFSDivision L2
FS Level 2NewOfficial PFSRevision Products

Functional Skills Maths Level 2 Book
Revise and practice for your functional skills maths level 2 exam. All topics covered in this compact functional skills maths revision guide book.

Functional Skills Maths Level 2 Mini Tests
Practice for your functional skills Maths level 2, questions from every topic included.

Functional Skills Maths Level 2 Revision Cards
Revise for functional skills maths level 2 easily and whenever and wherever you need. Covering all the topics, with revision, questions and answers for every topic.

Functional Skills Maths Level 2 Practice Papers
This 5 set of Functional Skills Maths Level 2 practice papers are a great way to revise for your Functional Skills Maths Level 2 exam. These practice papers have been specially tailored to match the format, structure, and question types used by each of the main exam boards for functional skills Maths. Each of the 5 papers also comes with a comprehensive mark scheme, so you can see how well you did, and identify areas to improve on.

Functional Skills Maths Level 2 Practice Papers & Revision Cards
This great value bundle enables you to get 5 functional skills maths level 2 practice papers along with the increasingly popular flashcard set that covers the level 2 content in quick fire format.