Functional Skills: Movement and Direction
Movement and Direction
In this section, we’ll look at movement and direction, as well as compass navigation.

Describing Rotational Movement
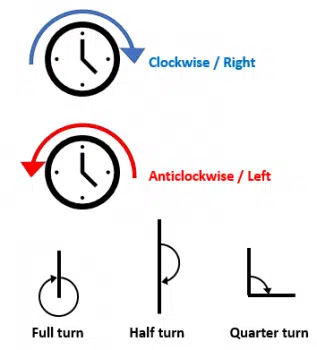
We have two opposite directions, clockwise and anticlockwise. We might also describe them as right and left, if the context is clearly referring to a rotational situation.
We also need to specify the size of movement. We’ll do this by comparing the size of a turn to the full turn of a clock i.e. 360°.
A half turn is 180° and a quarter turn is 90°.
Follow Our Socials
Our Facebook page can put you in touch with other students of your course for revision and community support. Alternatively, you can find us on Instagram or TikTok where we're always sharing revision tips for all our courses.

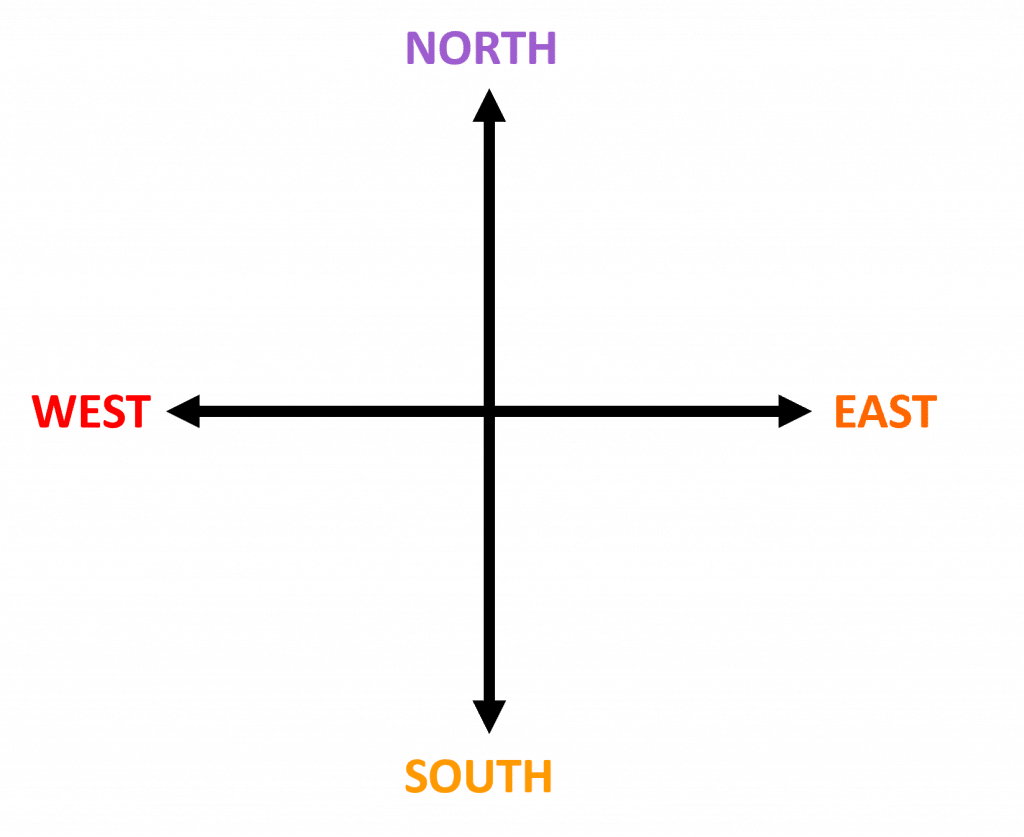

Four-Point and Eight-Point Compasses
The four directions on a four-point compass are North, East, South and West.
We have an easy mnemonic to remember them, too. Going from North and heading clockwise, we have:
Never Eat Shredded Wheat
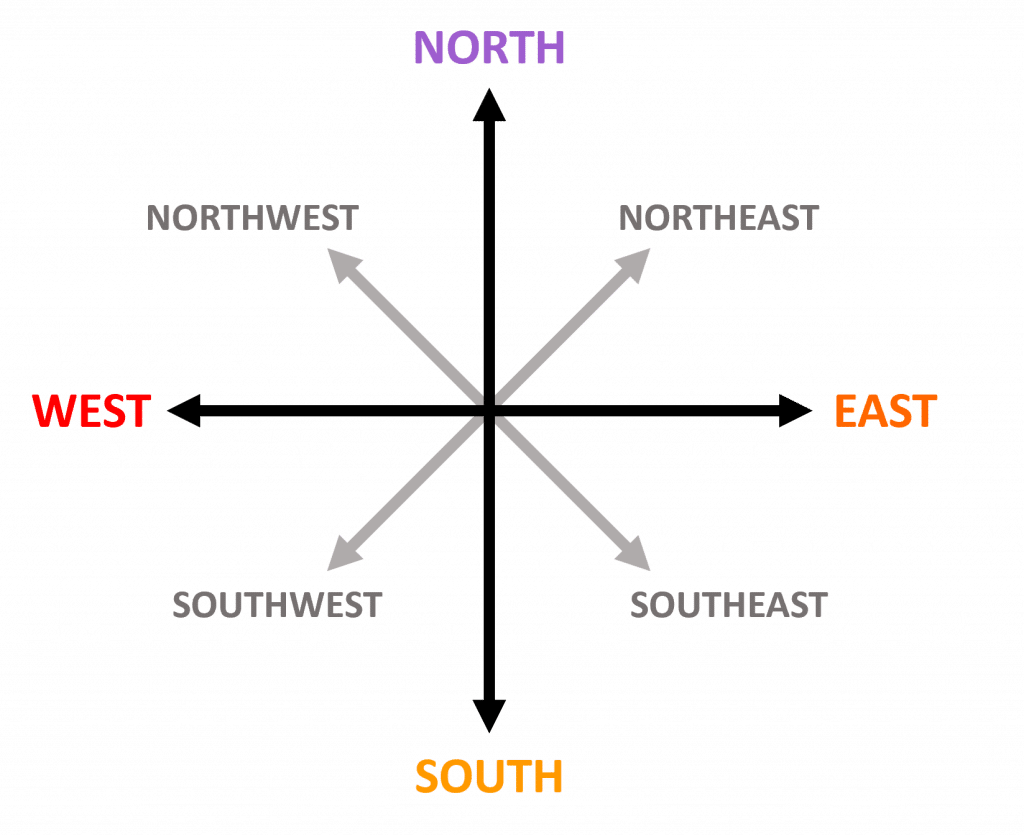

For an eight-point compass, we have our standard four directions, and four intermediate directions.
So, from North, East, South and West, we have the directions in between:
North-East, South-East, South-West and North-West.
Example 1: Describing Rotational Movement
A shower is set to the medium setting. What movement should be applied to turn the shower off?
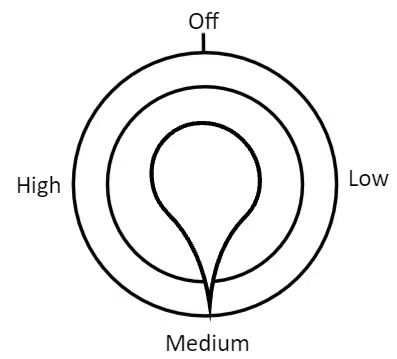
[1 mark]
This requires a half turn, in either direction.
Example 2: Four-Point and Eight-Point Compasses
The image below shows the direction of wind in Manchester.
What direction is this?
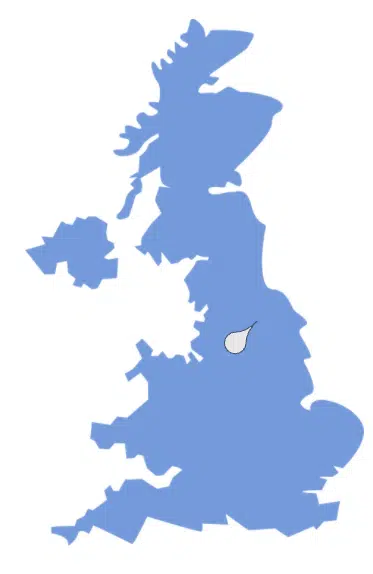
[1 mark]
The wind is moving in a northeasterly direction.
Functional Skills: Movement and Direction Example Questions
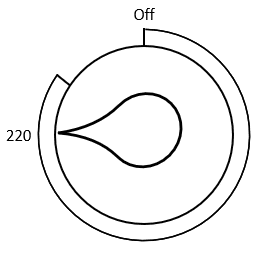
Question 1: A oven dial is set to 220 minutes. Given that the off setting cannot be reached by rotating to the right, describe fully the movement to switch it off.
[2 marks]
The off setting is a quarter turn clockwise from 220.
Since the off setting is not accessible this way, we must conclude that the off setting is three quarter turns anticlockwise from 220.
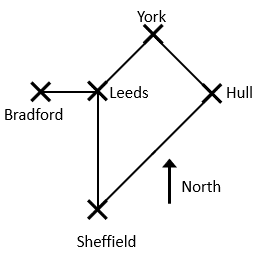
Question 2: Here’s a basic map of some Yorkshire cities, and the roads linking them.
Using the 8-point compass, and indicating all towns/cities on the way, indicate a route for:
a) Sheffield to York
b) Hull to Leeds
c) Bradford to Sheffield
[6 marks]
a) For Sheffield to York, the routes are:
Sheffield (N) to Leeds, Leeds (NE) to York
OR
Sheffield (NE) to Hull, Hull (NW) to York
b) For Hull to Leeds, the routes are:
Hull (NW) to York, York (SW) to Leeds
OR
Hull (SW) to Sheffield, Sheffield (N) to Leeds
c) For Bradford to Sheffield, the route is:
Bradford (E) to Leeds, Leeds (S) to Sheffield
(We could alternatively head East to Leeds and go clockwise around all remaining cities until Sheffield, but this is a little unnecessary.)
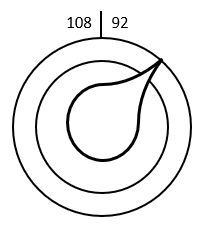
Question 3: The dial on a radio is turned so that it goes from 97.4\text{ Hz} to 101.4\text{ Hz}. Given that the radio ranges from 92\text{ Hz} to 108\text{ Hz} (which requires a full turn), describe fully the movement that the dial is turned to increase the frequency this way.
[3 marks]
The full turn from 92\text{ Hz} to 108\text{ Hz} is an increase of 16\text{ Hz}.
A turn from 97.4\text{ Hz} to 101.4\text{ Hz} is an increase 4\text{ Hz}.
Then this change is \dfrac{4}{16} of a turn, or \dfrac{1}{4} of a turn. The movement is a quarter turn clockwise.
Specification Points Covered
EL3.20 – Use appropriate positional vocabulary to describe position and direction including eight compass points and including full/half/quarter turns